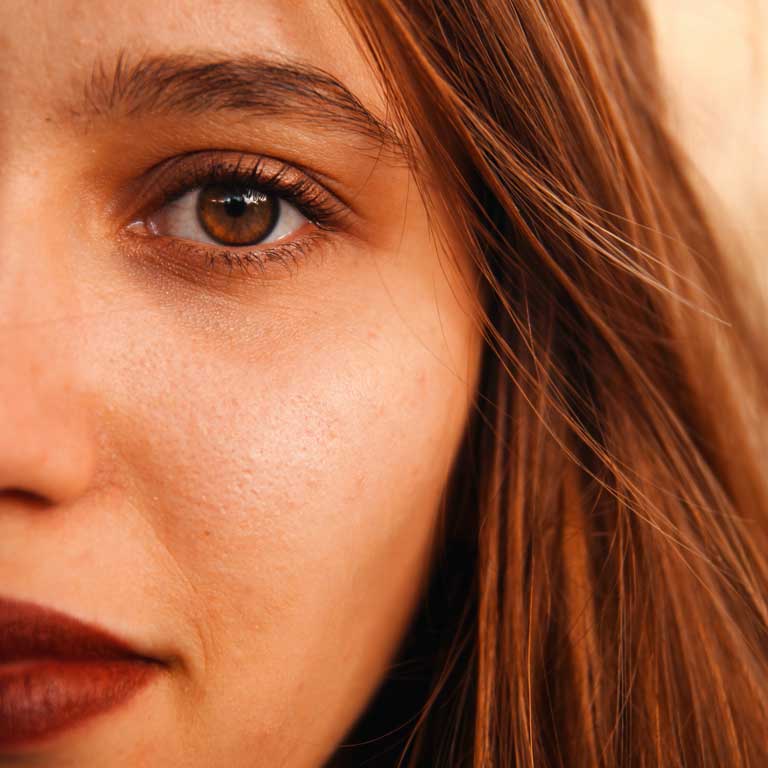

Vitamin A and Its Essential Role in Maintaining Healthy Vision
Vitamins and minerals are essential for the proper functioning of our bodies, and among them, Vitamin A stands out for its crucial role in supporting normal vision.
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin absorbed through the intestines and naturally present in many foods. It contributes not only to the immune system but, most importantly, to maintaining healthy eye function. One form of vitamin A, known as retinol, is a vital component of the eye’s structures and is essential for their normal operation.
According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, proper nutrition is key to maintaining the health of the retina and cornea, which are fundamental for good vision.
In today’s world, where many spend long hours in front of screens such as computers, televisions, and smartphones, eye care has become increasingly important. These habits often cause dryness and eye fatigue. Maintaining adequate vitamin A levels in the body supports the health of mucous membranes, especially those in the eyes, ensuring they stay moisturized and lubricated, which is critical for preserving their structure and function.
Why Is Vitamin A Important for Our Body?
Vitamin A plays a vital role in many processes within our body, but it is especially known for its involvement in cell division, iron metabolism, the immune system, skin health, and, as mentioned earlier, vision.
One of the most recognized functions of vitamin A is its essential contribution to maintaining normal visual function. It is crucial for the processes in the retina that allow us to form images in our brain based on what we see in our surroundings.
In addition, vitamin A also supports the maintenance of healthy skin cells, helping to keep the skin in good condition.
Maintenance of vision.
To maintain healthy visual function, having enough vitamin A is essential because it nourishes vital parts of the eye like the cornea and retina. This vitamin plays a crucial role in vision by participating in the production of retinal pigments that enable us to perceive the light spectrum.
Furthermore, adequate vitamin A levels help support good vision even in low-light conditions and assist the eyes in adapting to sudden changes in light.
What Are the Benefits of Vitamin A for the Skin?
In recent years, the benefits of vitamin A for the skin have led to its widespread use in moisturizers and high-concentration serums to enhance its local effects. The primary reason for applying vitamin A topically is its important role in maintaining the health of the skin and mucous membranes, as well as supporting cell regeneration.
Sources of Vitamin A in Our Diet
Vitamin A is naturally present in the foods we eat. It can be found in animal liver, whole milk, and other nutrient-rich animal products. It is also present in plant-based foods rich in carotenoids, which the body actively converts into vitamin A. Carotenoids are the pigments responsible for the colors of some fruits and vegetables, so a great source of vitamin A is found in orange and yellow foods.
Some of the foods highest in vitamin A include carrots, lettuce, bonito fish, red peppers, and eggs.
Forms of Vitamin A in Foods
Vitamin A in food comes in two main forms:
- Retinol: This form of vitamin A comes from animal-based foods. Since it is fat-soluble, it typically requires animal fat for absorption. Common sources include fish like salmon and calf liver.
- Carotenoids: Found in fruits and vegetables, these are plant-based sources of vitamin A. The most well-known example is the carrot, but others include spinach and pumpkin. Carotenoids are pro-vitamin A, meaning that when consumed, the body converts them into the active form of vitamin A.
Daily Recommended Intake of Vitamin A
The recommended daily intake of vitamin A varies primarily according to age and gender.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) suggests that adults aged 18 and over should consume between 0.65 milligrams and up to a maximum of 3 milligrams of Retinol Equivalents (RE) per day.
But what exactly does RE stand for?
RE means Retinol Equivalent, which indicates the amount of the active form of vitamin A, known as retinol. Another common unit used is the International Unit (IU), which measures a substance based on its biological activity. For vitamin A, the conversion is approximately 1 mg = 1818 IU.







